Dowsing theory
Dowsing = Mass attraction
Theory of operation:
Every particle of mass will emit an energy unique to only that element with the radius of the field being directly proportional to the mass. This energy will radiate outward in all directions which in turn will be induced into all adjacent materials. A mass laying on, or near, the surface will radiate the energy outward producing a spherical shaped field with the radius extending outward from the mass center.
The soil contained in the hemisphere below the surface becomes effectively the same chemical element of the target material. As the Earth's soil being the most significant material we can use the values to calculate the weight of the target mass. For example, 0.10 gram of silver laying on the ground will produce an energy field with a radius of 39 meters. The result is a hemisphere with an apparent mass of 136 million kg based on the weight of soil at 1098 kg per cubic meter.
An operator using a dowsing rod with a small sample of the target material coupled through the glass of a small vial will also induce an energy field into the surrounding soil. For example, a typical device producing an energy field of 12 meters will produce an apparent mass of 8 million kg. The energy field created by dowsing rod and the operator acts as a bandpass filter responding only to the wavelengths of the same element.
The masses of these two energy fields are attracted by mass attraction and follow the well-known laws of mass attraction as defined by Newton where the attractive force is directly proportional to the product of the masses, and inversely proportional to the square of the distance. The 0.1 gram of silver in the above example can be detected at an approximate distance of 750 meters.
One recent test using nickel calculated 304 ft to detect the sample while the actual test measured 316 ft. The area was largely over watered lawn so the ground contained slightly more mass than the values used in my calculations.
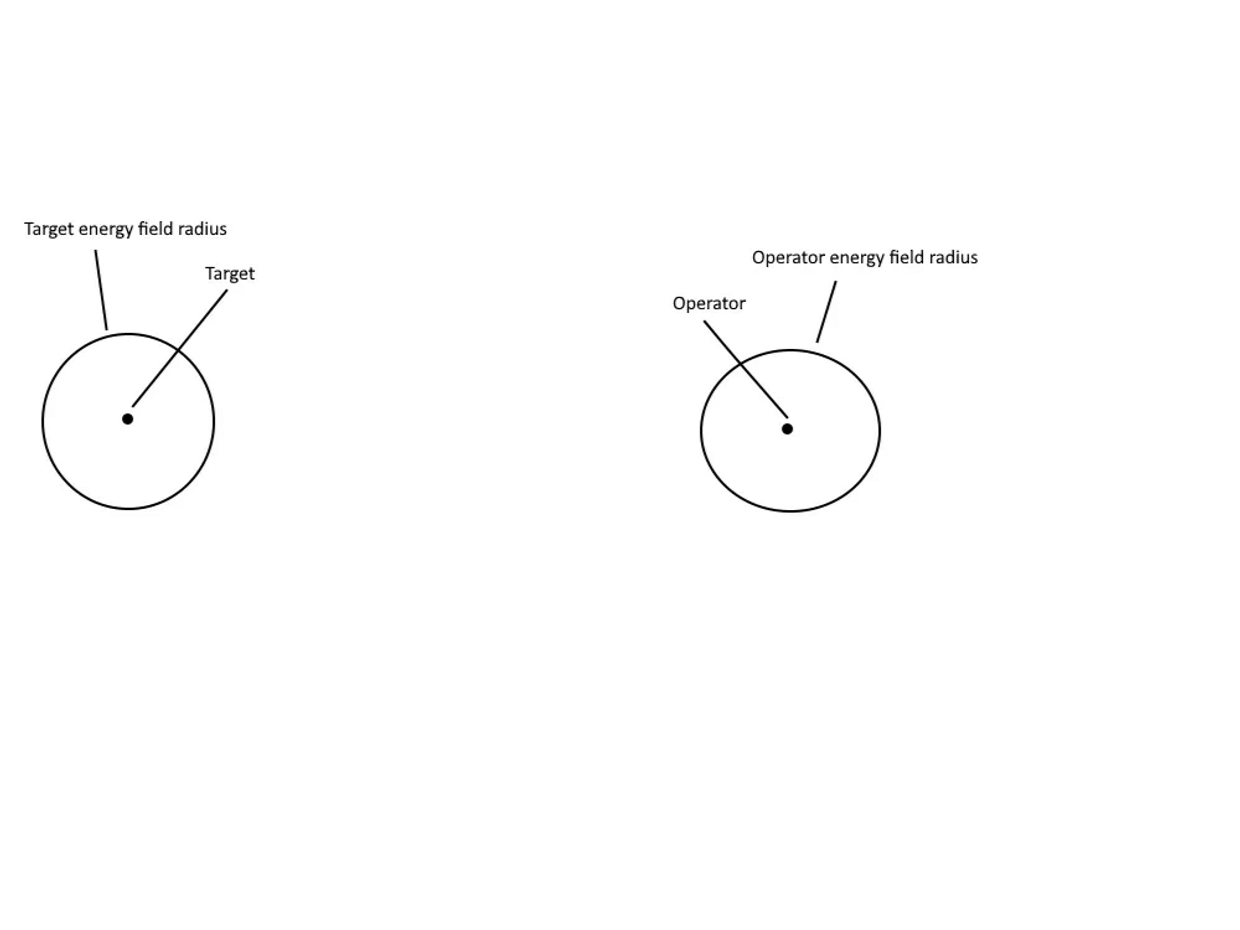
The left circle is used to represent the radius of the target energy field, The circle on the right is used to represent the radius of detector and operator energy field.